In the world of Windows administration, managing Group Policies is essential for maintaining security, configuration, and consistency across your network. If you’ve recently made changes to your Group Policy Objects (GPOs) and need them to take effect immediately, running the gpupdate command is your go-to solution. This article will walk you through everything you need to know about how to run a GPUPDATE to refresh Group Policies, ensuring your systems stay up-to-date and compliant.
Whether you’re an IT professional troubleshooting policy issues or a system administrator applying new settings, understanding gpupdate can save you time and frustration. For more in-depth resources on Windows tools and commands, check out our reference site at PGUPATE.IN.
What is Group Policy and Why Does It Matter?
Group Policy is a feature in Windows that allows administrators to manage user and computer settings centrally through Active Directory. It controls everything from password policies and software deployment to desktop configurations and security settings.
Group Policies are applied during computer startup, user logon, and at regular intervals (typically every 90 minutes with a random offset). However, if you need to apply changes right away—such as after editing a GPO—you’ll want to refresh them manually.
Refreshing Group Policies ensures that the latest configurations are enforced without requiring a reboot, making it a powerful tool for efficient management.
Why Refresh Group Policies with GPUPDATE?
There are several scenarios where you might need to run gpupdate:
- Immediate Application of Changes: After modifying a GPO in the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC), you don’t want to wait for the automatic refresh cycle.
- Troubleshooting: If policies aren’t applying as expected, refreshing can help identify and resolve issues.
- Testing New Policies: Quickly verify if new settings are working without restarting systems.
- Compliance and Security: Ensure critical updates, like security patches or restrictions, take effect promptly.
By using gpupdate, you can force a refresh of both computer and user policies, streamlining your workflow.
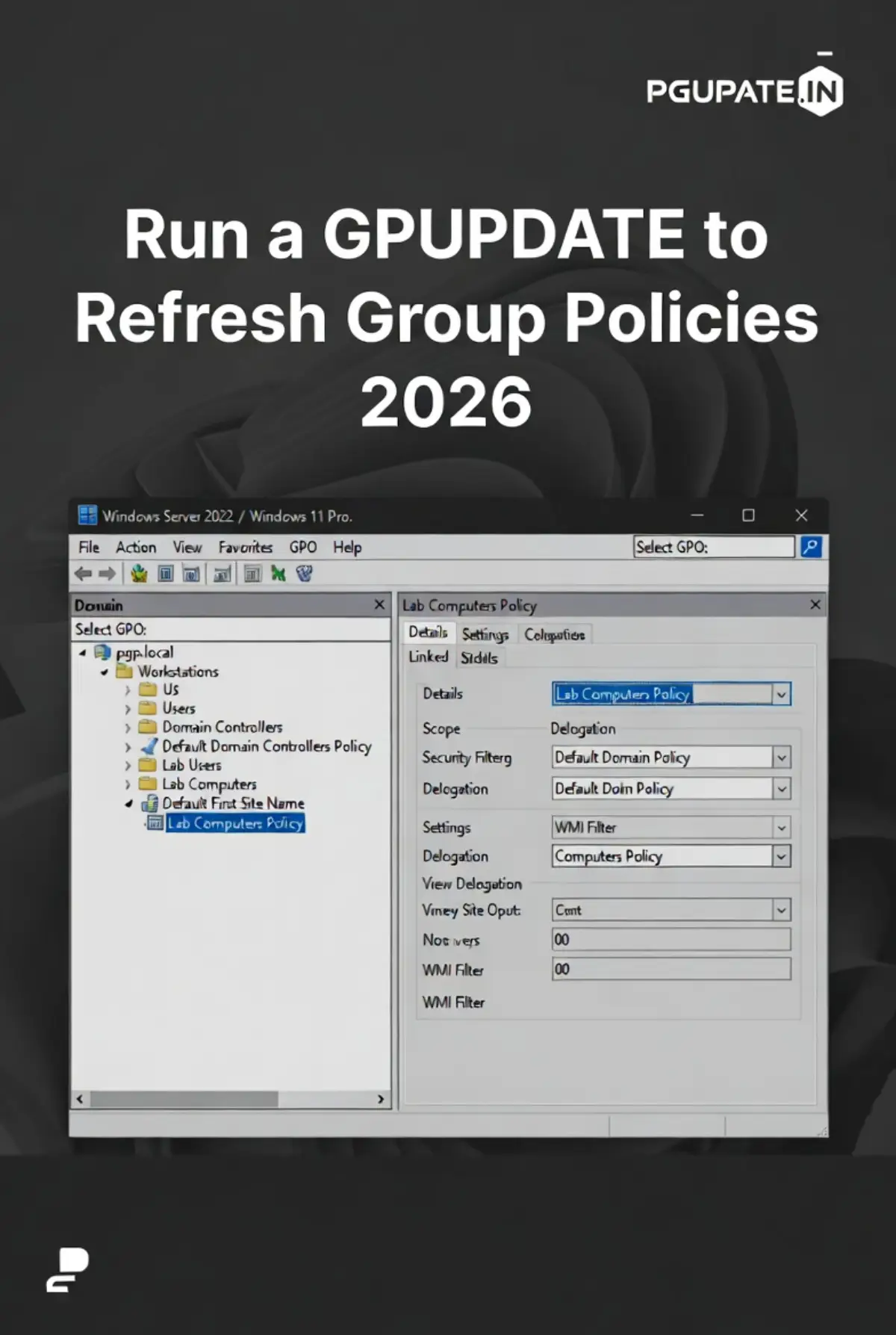
Windows Group Policy Management Editor interface Image: The Group Policy Management Editor where you can create and edit GPOs. Source: PGUPATE.IN
How to Run GPUPDATE: Step-by-Step Instructions
Running gpupdate is straightforward and can be done via the Command Prompt or PowerShell. Here’s how:
- Open Command Prompt as Administrator:
- Search for “cmd” in the Start menu.
- Right-click on Command Prompt and select “Run as administrator.”
- Run the Basic Command:
- Type gpupdate and press Enter.
- This refreshes both user and computer policies without forcing a reapplication.
- Use the /force Option for a Full Refresh:
- For a more thorough update, use gpupdate /force.
- This reapplies all policies, even if no changes were detected.
Note: You may need to log off and log back on for some user policies to fully apply, especially those related to user profiles.
Screenshot of running gpupdate command in Windows Command Prompt Image: Running the gpupdate command in Command Prompt. Source: PGUPATE.IN
Advanced GPUPDATE Command Options
The gpupdate command offers several switches to customize its behavior:
- /target {Computer | User}: Specifies whether to update only computer or user policies. Example: gpupdate /target:User.
- /force: Reapplies all policies, ignoring whether changes have occurred.
- /wait <value>: Sets a timeout in seconds for the command to complete (default is 600 seconds). Use -1 for no wait.
- /logoff: Automatically logs off after the update if required for policy application.
- /boot: Restarts the computer if policies require a reboot.
- /sync: Synchronizes the next foreground policy application (useful in domain environments).
For example, to force a refresh and log off if needed: gpupdate /force /logoff.
These options give you flexibility in various administrative scenarios. For detailed syntax and examples, visit PGUPATE.IN.
Output of gpupdate /force command in CMD Image: Output from running gpupdate /force, showing policy refresh status. Source: PGUPATE.IN
Troubleshooting Common GPUPDATE Issues
If gpupdate doesn’t work as expected, here are some tips:
- Access Denied Errors: Ensure you’re running as administrator.
- Policy Not Applying: Check for replication issues in Active Directory using repadmin /showrepl.
- Slow Refresh: Network connectivity problems might be the culprit—verify domain controller availability.
- Event Viewer Logs: Look in the System and Application logs for GroupPolicy events to diagnose errors.
If issues persist, tools like RSOP (Resultant Set of Policy) can help audit applied policies. More troubleshooting guides are available at PGUPATE.IN.
Best Practices for Managing Group Policies
To make the most of gpupdate:
- Test policies in a controlled environment before deploying widely.
- Use WMI filters or security groups to target policies precisely.
- Schedule regular audits of GPOs to avoid bloat.
- Combine with PowerShell scripts for automated refreshes in large networks.
By following these practices, you’ll maintain a robust and efficient Group Policy infrastructure.
Conclusion
Running a GPUPDATE to refresh Group Policies is a simple yet powerful way to ensure your Windows environment reflects the latest configurations. Whether you’re applying security updates or testing new settings, mastering this command will enhance your administrative efficiency.
For more Windows administration tips, tutorials, and tools, head over to PGUPATE.IN. If you have questions or need further assistance, drop a comment below!